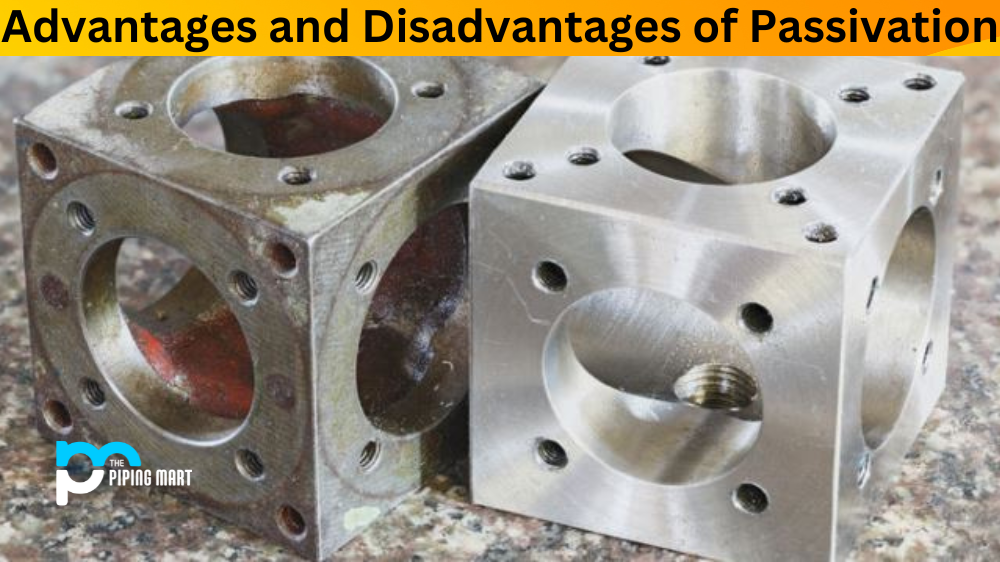
What is corrosion/rust?
Corrosion is a process that occurs naturally and converts the metal into its more stable version such as sulfide, carbonate, hydroxide, or oxide. Gradually it destructs the material by electrochemical or chemical reactions with the environment. Rusting is a well-known example of corrosion, rusting is a formation of iron oxide. It forms orange coloration on a surface which destructs the metal gradually. Also, corrosion influences the properties of the metal on a large scale that becomes dangerous for the metal. Reaction with hydrogen, oxygen, moisture, dirt, etc. is considered as the main cause of corrosion.
Types and causes of corrosion:
- Galvanic corrosion
Galvanic corrosion takes normally occurs near a joint when two dissimilar metals are in electronic contact. - Stress corrosion cracking (SCC)
Stress corrosion cracking occurs generally due to external stress such as actual tensile loads on the metal or expansion/contraction due to rapid temperature changes. Also, stress corrosion cracking (SCC) occurs due to a combination of corrosive temperatures and tensile strength at high temperatures. - Intergranular corrosion (IGC)
Intergranular corrosion is also known as IGC is generally caused due to impurities present at grain boundaries or in some cases due to depletion or enrichment of alloying elements near or at the grain boundary. - Crevice corrosion
Crevice corrosion generally occurs in that are shielded for example, under washers, gaskets, bolt heads, etc. it is a localized form of corrosion that results from a stagnant microenvironment, where there is a difference in there is a concentration difference of ions between two areas of metal. - Pitting corrosion
Pitting corrosion causes cavities or holes in the material, generally, it occurs by local Cathodic sites in an otherwise normal surface. It can be harmful by playing the role of stress risers. In simple language pitting corrosion is a form of corrosion that causes holes or pits in the metal. - Uniform corrosion
Uniform corrosion is the most common type of corrosion which is considered as an even attack across the surface of the material. This corrosion attack can be easily judged. This corrosion occurs generally on a large surface of the metal.
Which metals are corrosion resistant or don’t trust?
Some of the corrosion-resistant metals, their properties, general forms in which they are supplied, and applications are listed below:
Stainless steel:
Stainless steel is considered a material with excellent resistance to various corrosion in a wide range of corrosive atmospheres. Also, it is considered a green material as it is completely recyclable. Also, it is environmentally inert and neutral. Also, stainless steel has significant fire resistance when used in structural applications at a critical temperature above 800°C. products made from stainless steel are easy to clean and efficiently meets the requirements for decorative purposes as well as utensils used for cooking that requires frequent washing. Stainless steel is categorized as austenitic stainless steel, martensitic stainless steel duplex, PH grade stainless steel also known as precipitation hardening stainless steel, and ferritic stainless steel subcategorized in various grades.
Properties of stainless steel:
- Recyclable
- Low maintenance
- Good fabrication
- Easy formability
- Great durability
- Resistant to temperature
- High tensile strength
- Excellent corrosion resistance
Applications and uses of stainless steel:
Stainless steel is applicable in a wide range of industries and is preferable because of its remarkable properties especially resistance to corrosion. It has great demand and applications in aircraft, railcars, auto bodies, airport roofs, sculptures and monuments, bridges, architecture, dentistry, surgical implants, hemostats, cookware, cutlery, kitchen sinks, tanks, sinks, storage vessels, catalytic convertors, kiln, furnace, piping and pressure vessels, chemical storage tanks, expansion bellows, compensators, superheaters, food beverage equipment, washing machines, dishwashers, heat exchangers, paper and pulp industry, biofuel plants, marine industries and industries having high chloride-conditions, textile industry parts, chemical screens, oil refineries, flexible metal hose, firearms, fasteners, aircraft collector rings, jet engine parts, tubing, exhaust stacks and manifolds, saucepans, splashbacks, etc.
General forms in which stainless steel is supplied:
Stainless Steel is generally available in forms like sheets, plates, pipe, fittings and flanges, bar, quarto plate, tube, strip, etc.
Copper:
Word copper is derived from the Latin word cuprum, copper is considered as ductile, malleable, and soft metal having remarkably high conductivity to electricity. It is a chemical element with the symbol Cu, pure copper has a pinkish-orange color when freshly exposed. Also, copper is used as a constituent of a variety of metal alloys. Generally, it is found in nature in association with sulfur. A multistage process is performed to produce pure copper, usually from low-grade ores that contain copper sulfide. From the acid leaching of oxidized ores, an increasing share of copper is produced. Because of its corrosion resistance, thermal and electrical conductivity, malleability and high ductility copper is now the third most preferred industrial material. Also, copper can be easily worked and drawn into wires, due to this property it has a great demand in electric gadgets and similar industries.
Properties of copper:
- Atomic number – 29
- Electronegativity according to Pauling – 1.9
- Melting point – 1083°C
- Boiling point – 2595°C
- Vanderwaals radius – 0.128nm
- ionic radius – 0.096 nm (+1); 0.069 nm (+3)
- isotopes – 6
- easy to alloy
- catalytic
- recyclable
- attractive
- non-magnetic
- tough
- ductile
Applications and uses of copper:
copper is widely used in varieties of applications such as architecture, tubes, pipe, fittings, locks, scrapyard cranes, electric bells, pumps, vacuum cleaners, fridges, dishwashers, washing machines, cars, electric windows, windscreen wipers, starter motors, computers, fans, disc drives, DVD players, bicycles, electricity substations, mains adaptors, power stations, industrial machinery, copper roofing, plumbing, jewelry, etc.
General forms in which copper is supplied:
Copper is generally supplied in forms like copper strips, copper wire, ETP copper wire, continuous cast copper wire rod, CC rod, copper bars, copper flat bars, copper round bars, copper ingots, copper plates, etc. are widely supplied in the market.
Brass:
Brass is considered as a similar alloy to bronze, it’s an alloy of zinc and copper. 67% copper and 33% zinc are present in basic modern brass. Around 2% of lead is added to improve the machinability of brass. Brass is corrosion resistant and is usually used in applications that require low friction.
Properties of brass:
- Good ductility
- Easy to form
- Corrosion resistance
- High strength
- Antibacterial
- Higher malleability
- Low friction
- Low melting point
- Easy to cast
- Recyclable
Application and uses of brass:
Brass has wide usage in decorative and mechanical applications. It is commonly used in musical instruments such as bells and horns, electrical sockets and plugs, valves, hose couplings, plumbing, zippers, ammunition casing, bearings, gears, hinges, locks, fashion jewelry, costume jewelry, radiators, screws, architectural trim pieces, weather stripping, tubes, pipes, etc.
General forms in which brass is supplied:
Brass is generally formed as railings and handles, ammunition casing, marine hardware, plumbing fixtures, technical instruments, vehicle radiators, musical instruments, etc.
Bronze:
Tin and copper along with additional other metals are major components of bronze. Aluminum bronze, phosphor bronze, silicon bronze, leaded bronze, etc. are some of the common variants of bronze. It is considered as first used alloy by humans. Bronze is considered stronger compared to tin or copper alone. It is used in process of producing many parts of various types of machinery, as it has great durability and efficiency around air and water. Which makes it preferable in a wide range in various applications and industries.
Properties of bronze:
- Low metal to metal friction
- Highly resistant to seawater corrosion
- Has a melting point of 950°C.
- Good hardness
Applications and uses of bronze:
bronze is widely used in applications and industries like marine industries, fishing, musical instruments and sculptures, springs and electrical connectors, bearings and bushings, valves, gears, electrical components, bells, pump parts, mirrors, medals, and coins, etc.
General forms in which bronze is supplied:
Bronze is generally supplied as, Bronze Rod, Bronze bars (square, hexagon, and rectangular), Bronze pipes, Bronze wires (flat, round, and square), Bronze foils, Bronze coil, Bronze plates, Bronze sheets, and many more.

Pipingmart is B2B portal specializes in industrial, metal and piping products. Also, share latest information and news related to products, materials and different types grades to help business dealing in this industry.